Current conditions: Extreme rainfall in the Czech Republic could trigger some of the worst flooding in decades • South America has recorded more than 346,000 fire hotspots this year • A 4.7 magnitude earthquake rattled Los Angeles yesterday, followed by several aftershocks.
THE TOP FIVE
1. Global warming triggered a mega-tsunami that made the Earth vibrate for days
Back in September of last year, seismic sensors all over the world began detecting strange signals, the source of which researchers couldn’t identify. For nine days, the whole Earth appeared to vibrate at regular 90-second intervals. Now, scientists say they’ve figured out what happened: A massive landslide in Greenland, caused by a melting glacier, sent huge volumes of debris plummeting into a fjord and triggered a mega-tsunami. The energy from the wave remained trapped in the fjord for nine days, the water sloshing back and forth and sending vibrations rippling out across the entire globe. Here you can see before and after pictures of the glacier and the mountain:
 Science / Danish army
Science / Danish army
In a study published yesterday in the journal Science, the researchers explicitly link the event to climate change. Warming global temperatures caused the glacier to become too thin to support the mountain, so it collapsed. And they say there will be more events like these. “As we continue to alter our planet’s climate, we must be prepared for unexpected phenomena that challenge our current understanding and demand new ways of thinking,” the researchers wrote. “The ground beneath us is shaking, both literally and figuratively. While the scientific community must adapt and pave the way for informed decisions, it’s up to decision-makers to act.”
2. White House to host first Extreme Heat Summit today
The White House today will host its first-ever Extreme Heat Summit, where President Biden’s National Climate Advisor Ali Zaidi will issue an “Extreme Heat Call to Action,” urging leaders to step up their efforts to protect communities from the dangers of rising temperatures brought on by climate change. The summit comes on the heels of the hottest summer ever recorded in the Northern Hemisphere, and as the West Coast reels from wildfires made worse by drought and a record-breaking heat wave.
The summit will gather a variety of stakeholders – including emergency responders and health-care workers – to share takeaways and lessons from 2024’s extreme heat season, discuss how the government is helping and could help more, and identify gaps and opportunities for building extreme heat resilience ahead of next year. The White House will also announce a new “Community Heat Action Checklist” to serve as a roadmap to help leaders develop extreme heat plans.
“Climate-fueled extreme heat waves are showing up like wrecking balls in our communities, silently wreaking havoc on lives and livelihoods,” Zaidi said in a statement. “We recognize that this is climate change in action, and in response are taking a comprehensive approach to protecting both our people and infrastructure.” Investments from the Inflation Reduction Act and Bipartisan Infrastructure Law for helping states adapt to the effects of climate change, including extreme heat, total more than $50 billion.
3. Oxy gets $500 million from DOE for DAC hub
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Clean Energy Demonstrations has committed up to $500 million to help Occidental Petroleum’s carbon capture and sequestration unit 1PointFive develop its South Texas DAC Hub, Reutersreported. The hub will host Oxy’s first large-scale removal facility, which will aim to remove 500,000 metric tons of CO2 per year to start, ramping up to more than 1 million metric tons annually. “Occidental’s first large-scale DAC facility represents a pivotal economic trial for a technology that the International Energy Agency says will play a key role for global industrial decarbonization, despite its high costs in initial tests,” Reuters added.
Get Heatmap AM directly in your inbox every morning:
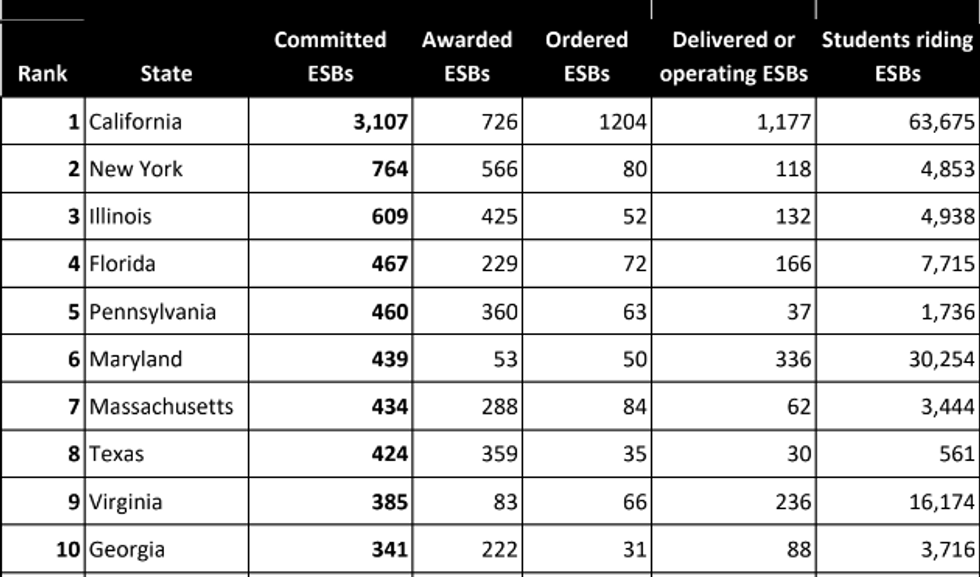
4. California leads in electric school bus deployments
A new report takes stock of state efforts to ditch diesel-powered school buses for electric fleets. Both federal and state funding is available to help with this transition. The report, from the Environment America Research and Policy Center and U.S. PIRG Education Fund, finds that California has the most “committed” electric school buses – that is, buses that have been awarded, ordered, delivered, or are already operational. The state has 1,777 e-buses up and running or ready to deploy, and is still waiting on nearly 2,000 more. These buses will serve more than 63,000 students. Also in the top five are New York, Illinois, Florida, and Pennsylvania, but they each trail California by quite a lot. Wyoming and Idaho are the only states with zero electric school buses. The report has lots of recommendations and tools to help school districts upgrade their fleets. It also urges students to pressure school boards to commit to making the switch.
5. Pharma companies are trialing new asthma inhalers that don’t warm the planet
Pharmaceutical companies are racing to get harmful pollutants out of their asthma inhalers, according to the Financial Times. Typical inhalers rely on propellants made from hydrofluorocarbons, or HFCs, to deliver life-saving drugs to users. But HFCs are potent greenhouse gases that are more effective than carbon dioxide at trapping heat in the atmosphere. Pharma giant GSK estimates its Ventolin inhaler accounted for nearly half of the company’s global carbon footprint in 2022, releasing the equivalent of 4.6 million metric tons of CO2. It’s developing a new inhaler that could have a 90% lower carbon footprint. Similarly, AstraZeneca has a new inhaler in the works that could cut 1.3 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent emissions annually. Both companies are trying to file for regulatory approval either by the end of 2024, or early next year.
THE KICKER
“Climate change is not a scientific or technical problem – it’s a political problem. And political problems can be solved by voting.” –Andrew Dressler, a climate scientist at Texas A&M, writing at The Climate Brink.